
- An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun or pronoun, often providing information about the qualities or characteristics of someone or something.
- Adjectives can describe these qualities independently or in comparison to something else, and they often appear directly before the noun or pronoun they modify. Examples include words like enormous, doglike, silly, yellow, fun, and fast.
- Adjectives have three forms: absolute (describing one thing, like messy), comparative (comparing two things, like messier), and superlative (indicating the highest degree, like messiest). Comparatives often use -er or more, while superlatives use -est or most.
- Coordinate adjectives equally modify the same noun and are separated by commas or conjunctions (long, cold winter). Non-coordinate adjectives form a unit of meaning and are not separated by a comma or conjunctions (tattered woolen sweater).
- Adjectives can also describe the quantity of nouns: many, few, millions, eleven.
Here, we’ll explore adjectives, how they function, and provide examples to help you use them effectively.
Table of contents
Nouns as adjectives and adjectives as nouns
Adjective definition
An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun, providing additional information about its qualities, characteristics, or attributes. For example, in the phrase “the tall building,” the adjective tall gives specific details about the building’s height.
Adjectives can convey various aspects, such as size, color, shape, and emotion, enhancing the meaning of the nouns they accompany.
How to use adjectives
Use adjectives to tell the reader what kind of something you’re talking about or how much or how many of something you’re talking about.
Three and white are modifying flowers.
Often, when adjectives are used together, you should separate them with a comma or conjunction. See “Coordinate adjectives” below for more details.
Adjectives modify nouns
As you may already know, adjectives are words that modify (describe) nouns. Adjectives do not modify verbs, adverbs, or other adjectives.
The adjectives are easy to spot in the sentences above because they come immediately before the nouns they modify.
However, adjectives can modify nouns without appearing before them in a sentence. Acting as a subjective complement with the help of a linking verb, a predicate adjective modifies the subject of a sentence.
A linking verb is a verb like to be, to feel, to seem, or to taste that, rather than describing an action, helps to describe a state of being or a sensory experience.
Degrees of adjectives
Adjectives come in three forms, known as degrees: absolute, comparative, and superlative.
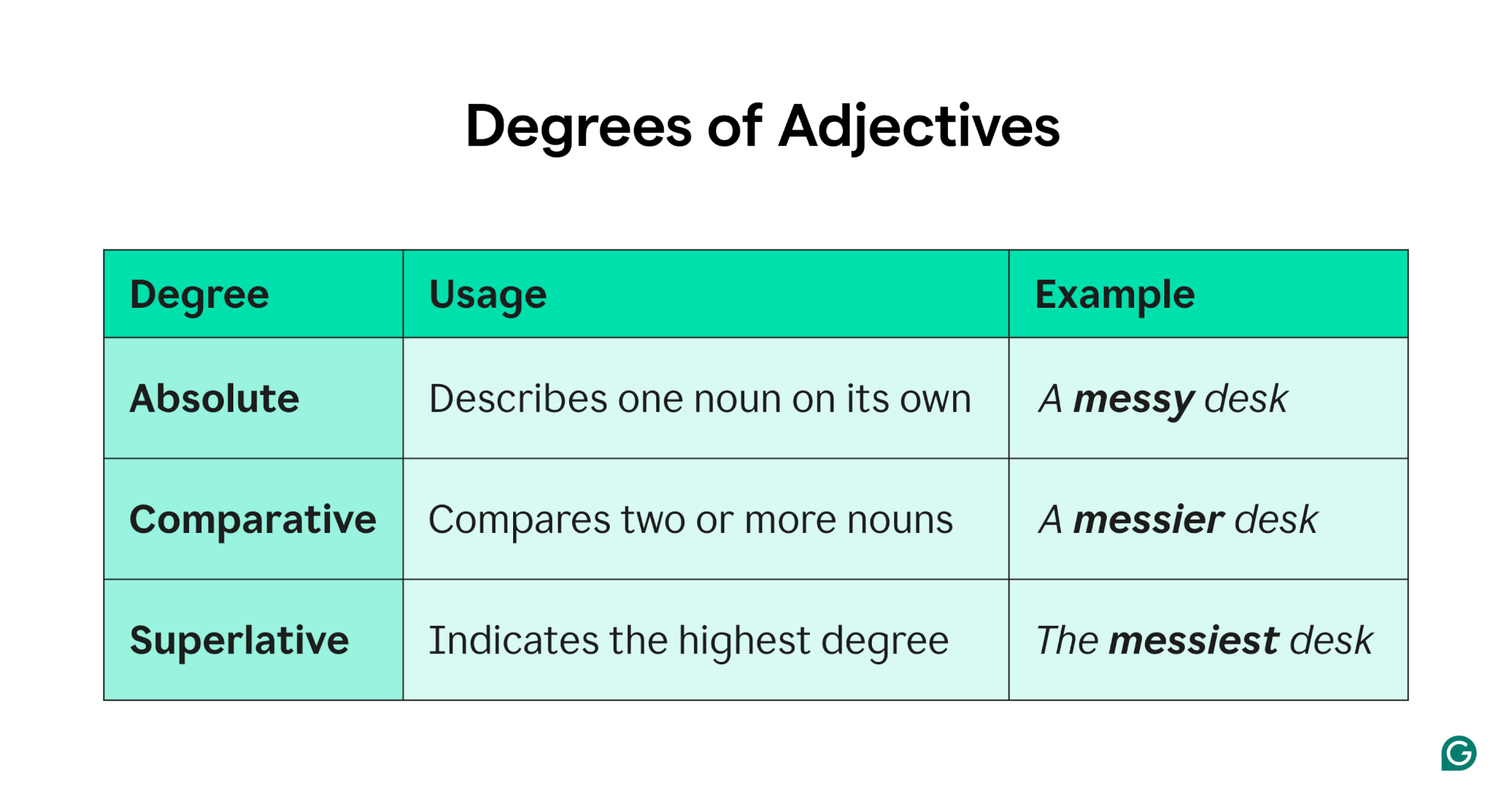
Absolute adjectives
Absolute adjectives express a quality in an extreme or absolute sense, leaving no room for degrees of comparison. They describe qualities that cannot typically be modified or intensified.
Examples of absolute adjectives
Comparative adjectives
Comparative adjectives, unsurprisingly, make a comparison between two or more things. For most one-syllable adjectives, the comparative is formed by adding the suffix -er (or just -r if the adjective ends with an e).
For two-syllable adjectives, some use -er to form the comparative, while others use the word more. In general, two-syllable adjectives ending in -er, -le, -ow, -ure, or -y can be made comparative by adding -er (in the case of -y words, replace y with -ier). For adjectives of three or more syllables, add the word more.
Examples of comparative adjectives
Superlative adjectives
Superlative adjectives indicate that something has the highest degree of the quality in question. One-syllable adjectives become superlatives by adding the suffix -est (or just -st for adjectives that already end in e).
As with the comparative, some two-syllable adjectives use -est to form the superlative, while others use the word most. Generally, two-syllable adjectives ending in -y replace -y with -iest.
Adjectives of three or more syllables add the word most. An article with a superlative adjective will almost always be the definite article (the) rather than the indefinite articles a or an. Using a superlative inherently indicates that you are talking about a specific item or items.
Examples of superlative adjectives
Coordinate adjectives
Coordinate adjectives should be separated by a comma or the word and. Adjectives are said to be coordinate if they modify the same noun in a sentence to the same degree.
Sometimes, when two adjectives appear next to each other and modify the same noun, the one closer to the noun is so closely related to the noun that they form a single semantic unit together. That unit is what is modified by the first adjective. In this case, the adjectives are not coordinate and should not be separated by a comma.
In some cases, it’s pretty hard to tell whether two adjectives are coordinate or not. But there are a couple of ways you can test them. Try inserting the word and between the adjectives to see if the phrase still seems natural.
In the first sentence above, “this tattered and woolen sweater” doesn’t sound right because you aren’t talking about a sweater that is both tattered and woolen in the same way. It’s a woolen sweater inherently, and it has become tattered. Woolen sweater forms a unit of meaning that is modified by tattered.
Another way to test for coordinate adjectives is to try switching the order of the adjectives and seeing if the phrase still works. In the second sentence, you wouldn’t say, “No one could open the silver old locket.” You can’t reverse the order of the adjectives because silver locket is a unit modified by old.
Order of adjectives
When combined in a sentence, adjectives follow a specific order:
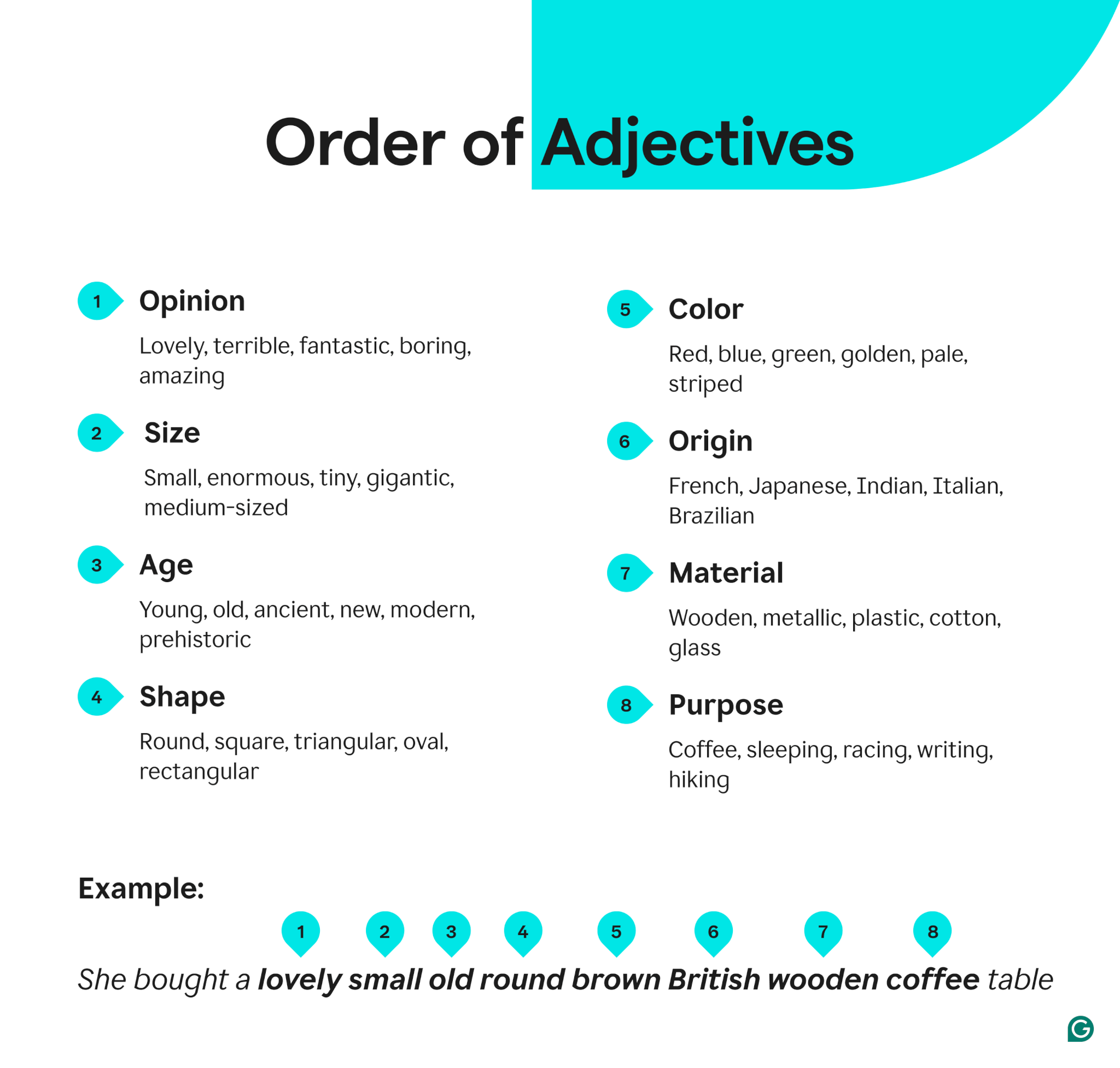
In English, the rules regarding adjective order are more specific than in other languages; that is why saying adjectives in a particular order sounds “right,” and deviating from that order makes a statement sound “wrong,” even if it’s otherwise grammatically perfect.
Compound adjectives
Compound adjectives combine two or more words to act as a single descriptor for a noun, often linked with hyphens to ensure clarity. The hyphen helps show that the words work together to modify the noun, preventing potential confusion.
When the compound adjective follows the noun, the hyphen is typically dropped:
Adverbs modifying adjectives are not typically hyphenated. Instead, they are written separately.
Common compound adjective forms include the following:
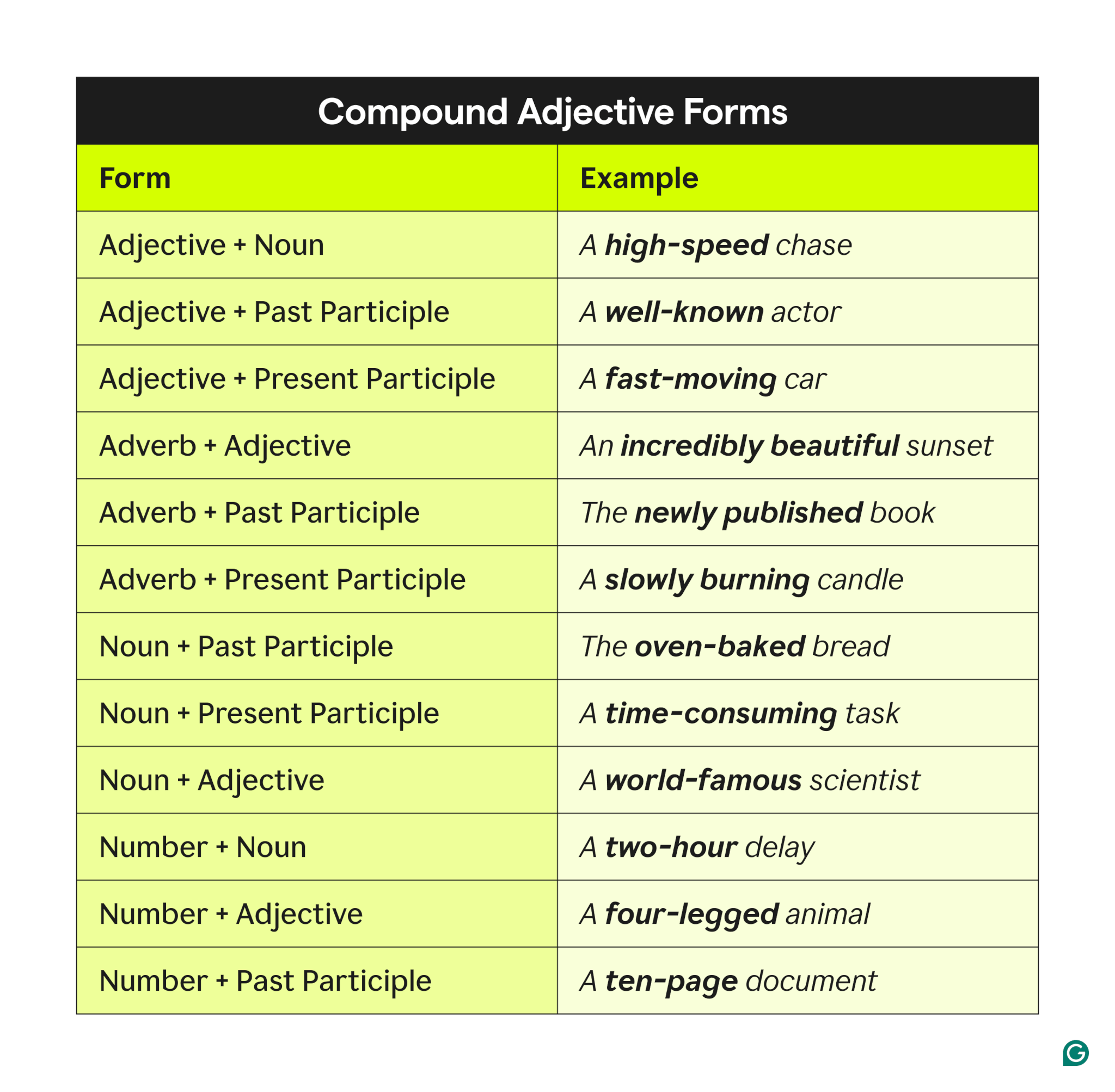
Using hyphens in compound adjectives when appropriate ensures precision and readability, especially when the meaning might otherwise be unclear.
Adjectives vs. adverbs
Many of us learned in school that adjectives modify nouns and adverbs modify verbs. But as we’ve seen, adjectives don’t need to be right next to nouns to modify them; they can do so after a linking verb in a sentence as predicate adjectives.
This leads to a common type of mistake: using an adverb when what you want is a predicate adjective. Here’s an example you’ve probably heard before:
Because feel is a verb, it may seem to call for an adverb rather than an adjective. But feel isn’t just any verb; it’s a linking verb. An adverb would describe how you perform the action of feeling—an adjective describes what you feel.
“I feel badly” would mean you are bad at feeling things. If you’re feeling numb, it might make sense to say, “I feel badly.” But if you’re trying to say that you are experiencing a negative emotion, “I feel bad” is the phrase you want.
It’s easier to see this distinction with a different linking verb. Consider the difference between these two sentences:
“Max smells badly” means that Max has a weak sense of smell. “Max smells bad” means that Max stinks.
Nouns as adjectives and adjectives as nouns
One more thing you should know about adjectives is that, sometimes, a word normally used as a noun can function as an adjective, depending on its placement.
Guide is a noun, but in this sentence, it is used as an adjective to modify dog.
It works the other way, too: Sometimes, words that are normally adjectives shift into use as nouns. Many times, this happens with adjectives used to denote a group of people, with the addition of the:
The word people has been omitted in the above examples, and the adjectives French, rich, and poor function as nouns. This kind of shift also happens with other types of adjective-noun pairs, especially when they are commonly used together:
In these sentences, the nouns exam and qualities have been omitted.
Adjective usage advice
It’s one thing to know how to use an adjective; it’s another to know when using one is a good idea. Good writing is precise and concise.
Sometimes, you need an adjective to convey precisely what you mean. It’s hard to describe a “red sports car” without the word red. But often, choosing the right noun eliminates the need to include an adjective. Is it “a big house” or “a mansion”? “A large crowd” or “a throng”? “A mixed-breed dog” or “a mutt”? “A dark night” or just “night”?
Always aim to make every word count in your writing. If you need an adjective, use it. But if it’s not adding value, skip it.
Adjective FAQs
What is an adjective?
An adjective is a word that describes the traits, qualities, or number of a noun.
What are examples of adjectives?
Descriptive words like beautiful, smooth, and heavy are all adjectives, as are numbers (twelve eggs).
What is the difference between adjectives and adverbs?
Adjectives modify nouns, while adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. For example, in the phrase very funny movie, funny is an adjective describing the noun movie, and very is an adverb describing the adjective funny.
Can adjectives modify adverbs?
Adjectives can modify only nouns. Only adverbs can modify other adverbs.






