Key takeaways
- AI detectors estimate the likelihood that text was AI-generated, but they’re not 100% accurate.
- Accuracy depends on factors like writing style, AI model complexity, and training data quality.
- Combine AI detection with proper citation practices and additional tools like Grammarly Authorship and plagiarism detection.
As more people use artificial intelligence (AI) to write and publish content, AI detectors have emerged in an effort to provide transparency. They’re used to estimate the likelihood that text was generated by AI. But how accurate are these detectors? While many people, including students, educators, and professionals, seek reliable methods to determine AI-generated content, AI detection tools are not foolproof. Their accuracy varies based on several factors so they should be used alongside other originality-checking methods.
In this article, we’ll explore how AI detectors work, their limitations, and the best practices for using them responsibly to support academic integrity and content authenticity.
Table of contents
Factors influencing detector accuracy
Evaluating AI detector accuracy
Why AI detectors aren’t always accurate
Future of AI detection accuracy
How Grammarly’s AI detection works
Best practices for using AI detectors
Understanding AI detectors
AI detectors estimate the likelihood that content—whether text, images, code, or multimedia—was generated by artificial intelligence. They analyze patterns, structures, and metadata to differentiate AI-created content from human-produced work. These tools are used in various industries for content verification, fraud detection, and media authentication. However, because technology is constantly evolving, AI detection is inexact. For this reason, AI detection tools are most effective when used alongside other methods, such as plagiarism detection, citations, and authorship tracking, to provide a more comprehensive assessment of content originality.
How AI detectors work
AI detectors use machine learning models trained to recognize patterns of AI-generated content. Most models are developed using large datasets of both AI- and human-generated text, which allows them to identify differences between the two. AI detectors analyze elements such as sentence structure, predictability, repetition, and metadata traces that may indicate AI involvement. Some tools also compare content against known AI outputs to gauge similarity. However, because AI-generated text can closely mimic human writing, detection results are not 100% accurate.
Some of the key techniques used in AI detection include:
- Perplexity and burstiness analysis, which measures how predictable and varied a text is compared to typical AI-generated content.
- Pattern matching, which identifies text similarities compared to known AI-generated content.
- Statistical modeling, which uses machine learning algorithms to estimate the probability of AI involvement.
While these methods provide insights, they can sometimes produce inaccurate results. AI detection should be used alongside other originality tools, such as plagiarism detection and authorship verification, to ensure a more comprehensive assessment of content integrity.
Factors influencing AI detector accuracy
No AI detector can guarantee definitive results. Accuracy depends on multiple factors:
Quality of training data
AI detectors rely on large datasets of both human-written and AI-generated content. The quality, diversity, and recency of these datasets can significantly influence the tool’s effectiveness. If a detector is trained on outdated, limited, or biased data, it may produce inaccurate results.
Algorithmic approaches
AI detection tools use various machine learning techniques to assess text. Some rely on simple rule-based models, while others use deep learning. The type of algorithm influences how accurately the detector distinguishes between human- and AI-generated text. Additionally, some methods may introduce biases, particularly against writers who speak English as an additional language.
Complexity of AI models
As AI writing models evolve, detecting AI-generated text becomes increasingly difficult. Newer AI systems produce more sophisticated, human-like writing, making it harder for detectors to differentiate between human and AI text accurately. Ongoing advancements in AI mean detection tools must continuously adapt, yet they will always lag behind.
Evaluating AI detection accuracy
When assessing the reliability of AI detection tools, consider the following criteria:
- False positives: False positives occur when human-written content is incorrectly flagged as AI-generated.
- False negatives: False negatives occur when AI-generated content is mistakenly classified as human-written.
- Consistency: Does the tool produce the same results across similar inputs? If not, it may not be accurate.
- Transparency: Does the tool provide an explanation for its findings? An added layer of transparency can help you determine how to proceed with verifying the content.
No AI detector can achieve perfect accuracy. False positives and false negatives highlight the importance of using AI detection tools cautiously and in conjunction with other originality verification methods.
Why AI detectors aren’t always accurate
AI detection faces several challenges that impacts its reliability, including:
- Bias in AI detection models: Some detectors are more likely to flag writing from people who speak English as an additional language.
- Inability to keep pace with evolving AI technology: As AI-generated text becomes more sophisticated, detection models may struggle to differentiate between AI and human writing. They will always lag behind the latest AI model.
- Lack of transparency: Many AI detectors do not explain why they flagged certain text, making it harder to interpret the results.
Limitations of AI detectors
While AI detection tools offer valuable insights into writing patterns, they have significant limitations:
- Inaccuracy: No AI detector is 100% reliable. AI detectors estimate the likelihood that the text was AI-generated. They do not track authorship, which means even human-written text can be flagged as AI-generated. Meanwhile, lightly edited AI-generated text may evade detection. As a result, AI detection should never be used as a standalone verification method.
- Potential bias: Some AI detectors disproportionately flag writing from people who speak English as an additional language due to linguistic differences.
- Misuse and overreliance: Relying solely on AI detection to determine authenticity can lead to unjustified accusations of AI misuse.
Future advancements in AI detection accuracy
As AI-generated text continues to evolve, researchers and developers continue to refine detection methods. Future advancements aim to improve reliability, reduce bias, and provide greater transparency. The following advancements aim to make AI detection more effective in the future:
- More robust AI training datasets: Expanding datasets to better reflect diverse writing styles will help mitigate bias and improve detection.
- Better explanations for results: Providing clearer reasoning behind AI-generated content flags can help writers and readers alike know how to move forward with editing work or verifying originality.
- Integration with other originality tools: The best to improve AI detection is to combine automated content flagging with AI citations and authorship tracking.
How Grammarly’s AI detection works
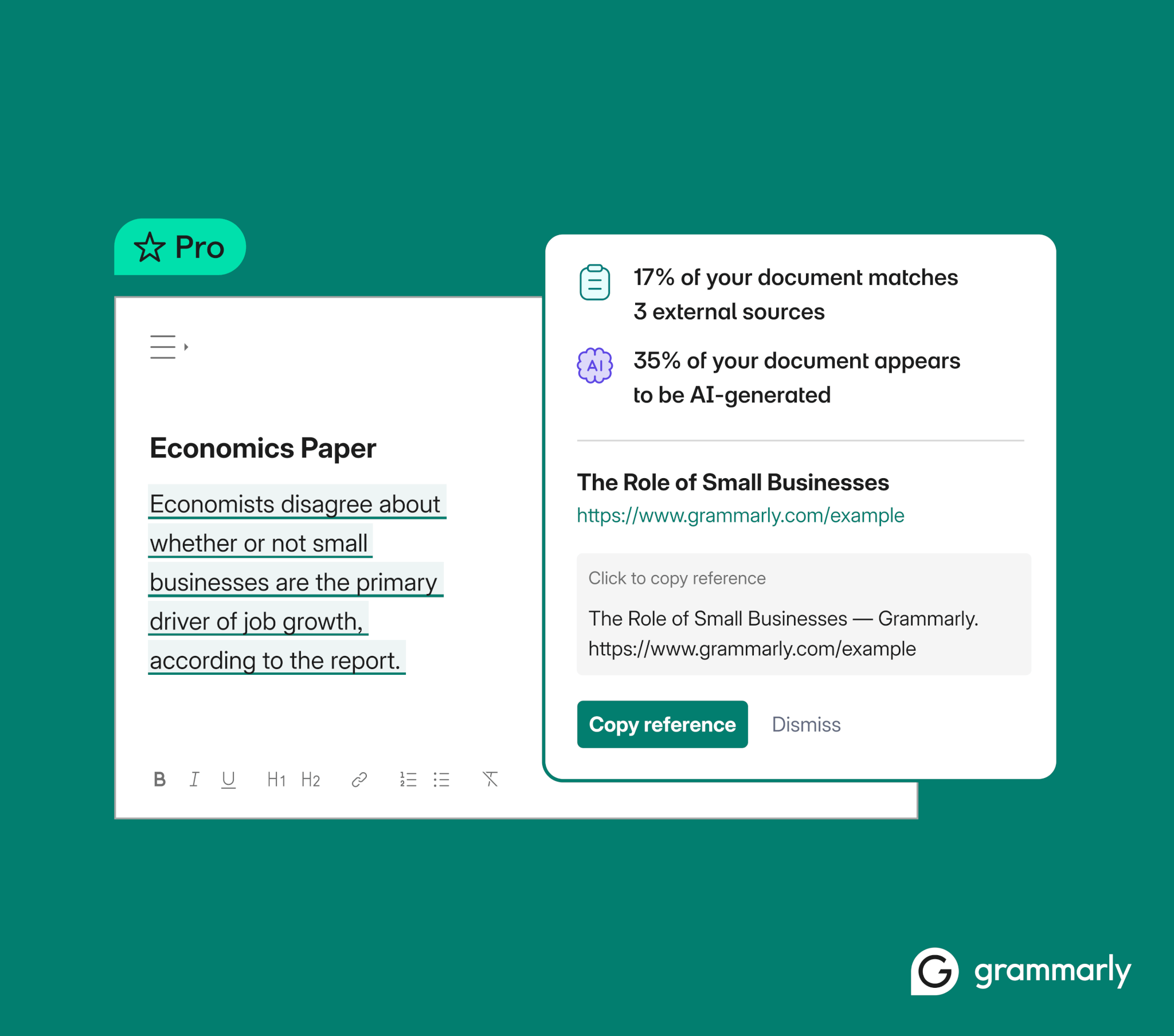
We designed Grammarly’s AI detection to provide transparency into the likelihood that a piece of writing contains AI-generated content. When Grammarly scans a document, it breaks the text into smaller sections and analyzes each one for language patterns commonly associated with AI-generated content. We trained our AI detection on tens of thousands of AI-generated texts and content written by humans before 2021, allowing it to identify distinguishing patterns between the two. Based on this analysis, it provides a percentage score indicating the proportion of the document that may be AI-generated.
Our AI detector is just one of many features we offer to support responsible AI use. We also provide writers with AI citations so they can properly cite when and how they used AI and Grammarly Authorship, which allows them to track how their document was created.
Grammarly offers several features to support transparency and originality in writing:
- Citations: Our citation generator allows users to properly attribute AI-assisted content so writers can be transparent about their AI use.
- Plagiarism detection: Our plagiarism checker compares text against a vast database of online sources to identify potential instances of uncredited content.
- Grammarly Authorship: For a more verifiable approach to measuring authenticity, Grammarly Authorship tracks how a piece of content was created. Once turned on, Authorship categorizes content based on its origin and provides a report that shows the percentages of text that was typed by a human, generated with AI, or pasted from external sources and edited.

Best practices for using AI detectors
AI detectors can be useful tools, but they should be used thoughtfully. Using AI detectors wisely helps maintain accuracy, fairness, and ethical decision-making. We recommend the following best practices for working with AI detectors to verify content originality:
- Recognize limitations. AI detectors are not 100% accurate and may produce false positives or negatives. Use them as a guide, not a final verdict.
- Verify with multiple tools. Different detectors have varying accuracy. Cross-checking results can help reduce misclassification.
- Understand AI writing patterns. AI-generated content often has repetitive phrasing and lacks nuance. Recognizing these signs can help interpret results.
- Consider context, intent, and writing style. A flagged result should prompt further review, not immediate action. Take into account the writer’s typical style, voice, readability, and phrasing. If the text differs significantly from their previous work, AI detection can serve as a check on initial suspicions but should not be the sole determinant.
- Be transparent. Clearly communicate the role AI detection plays in grading or verifying content. Create guidelines for editors and educators so they don’t overrely on AI detectors when making decisions.
- Use AI detection alongside other originality tools. AI detection is most effective when paired with plagiarism detection, citations, and features like Grammarly Authorship.
Conclusion
So, are AI detectors accurate? While AI detectors can provide helpful insights, they are not accurate 100% of the time and should not be the sole measure of originality. AI detection tools work best when used as part of a broader strategy for verifying content and when paired with clear guidelines for responsible AI use. Grammarly offers a holistic approach to content originality that includes plagiarism detection, AI citations, and authorship tracking, which allows writers to provide transparency and uphold integrity in writing. As AI technology continues to evolve, so too will AI detection. Ultimately, responsible AI use, institutional guidance, and informed decision-making remain essential.
AI detection FAQs
How do AI detectors work?
AI detectors analyze text patterns, sentence structures, and style choices to estimate the likelihood that content was generated by AI. They use machine learning models trained on large datasets of AI-generated and human-written text to identify differences between the two. The tools use these patterns to assess text, but their accuracy can vary.
How accurate are AI writing detectors?
No AI detector is 100% accurate, so you should never rely on the results of an AI detector alone to determine whether AI was used to generate content. AI detectors can identify language patterns that seem robotic or generic, potentially indicating the use of AI, but they cannot definitively conclude whether or not AI was used. These tools should be one part of a holistic approach to evaluating originality.
Can an AI detector be wrong?
Yes, AI detectors can be wrong. AI detectors rely on statistical patterns rather than deep comprehension, meaning they may misclassify text that is overly formal, repetitive, or lacks personal nuance. Writers who speak English as an additional language are particularly vulnerable to misclassification because their writing may differ from the datasets used to train AI detectors. Because of this inherent bias, context, manual review, and additional verification tools are essential when assessing content originality.
Should I rely on AI detectors to verify content authenticity?
AI detectors can provide insight, but they should not be the sole method for verifying content authenticity. We recommend combining automatic AI detection with manual review, and encourage writers to track their writing process with Grammarly Authorship and provide proper attribution when they use AI.