
- A metaphor is a figure of speech that compares two different things by stating that one is the other, highlighting similarities for emphasis or symbolism.
- The compared elements are not literally the same but are linked to create a deeper understanding or evoke imagery.
- Metaphors help convey abstract concepts, emotions, or complex ideas through vivid and imaginative language.
- They are commonly used in speech, poetry, literature, and everyday communication to add depth and expressiveness.
- Unlike a simile, which uses like or as, a metaphor makes a direct comparison, strengthening the connection between ideas.
Below, we explain everything you need to know about metaphors, including their types, uses, and plenty of examples to illustrate them.
Table of contents
Metaphor definition
A metaphor is a figure of speech that directly compares two unrelated things by stating that one is the other. Metaphors can be objects, actions, or ideas that are used to symbolize something else.
Metaphors are a form of figurative language, which refers to words or expressions that mean something different from their literal definition. Abstract ideas can be challenging to put into words, so comparing them with something easier to understand is often useful.
In the case of metaphors, the literal interpretation often sounds odd. For example, imagine what these metaphors would look like if you took them literally:
These metaphors create more robust descriptions of people or events than bland phrases like “love is difficult” or “Silas is kind and generous.”
Metaphors show up in literature, poetry, and music, but also in speech. If you hear someone say “metaphorically speaking,” it probably means that you shouldn’t take what they said as the literal truth but as more of an idea.
For example, let’s say it’s finals period, and after exams, students are saying things like, “That test was murder.” It’s a fair guess they’re still alive if they’re commenting on the test, so this is an example of people speaking metaphorically or figuratively.
Examples of metaphors
As common figures of speech, metaphors turn up everywhere, from novels and films to presidential speeches and even popular songs. When they’re especially good, they’re hard to miss.
Examples of metaphors in everyday speech
Examples of metaphors in literature
Examples of metaphors in history
Examples of metaphors in pop culture
Metaphor vs. simile
Metaphors are closely related to similes; both are figures of speech that compare two things. The key difference is that similes use the words like or as to make a direct comparison, while metaphors do not.
Similes explicitly state that two things are similar, highlighting their resemblance. In contrast, metaphors imply that one thing is another, creating a figurative connection that the reader or audience must interpret.
- Metaphor: When I wake up in the morning, I’m a zombie.
- Simile: When I wake up in the morning, I’m as slow as a zombie.
While including like or as in a comparison may seem minor, it creates a significant distinction. Metaphors tend to be more powerful and poetic because they require the audience to interpret the figurative connection on their own. On the other hand, similes make the comparison more explicit, reducing the chance of misinterpretation by being more direct and less nuanced.
Here are some more examples of similes:
Types of metaphors
There are many different types of metaphors and even more strategies to use them all. Let’s focus on a couple of the most common.
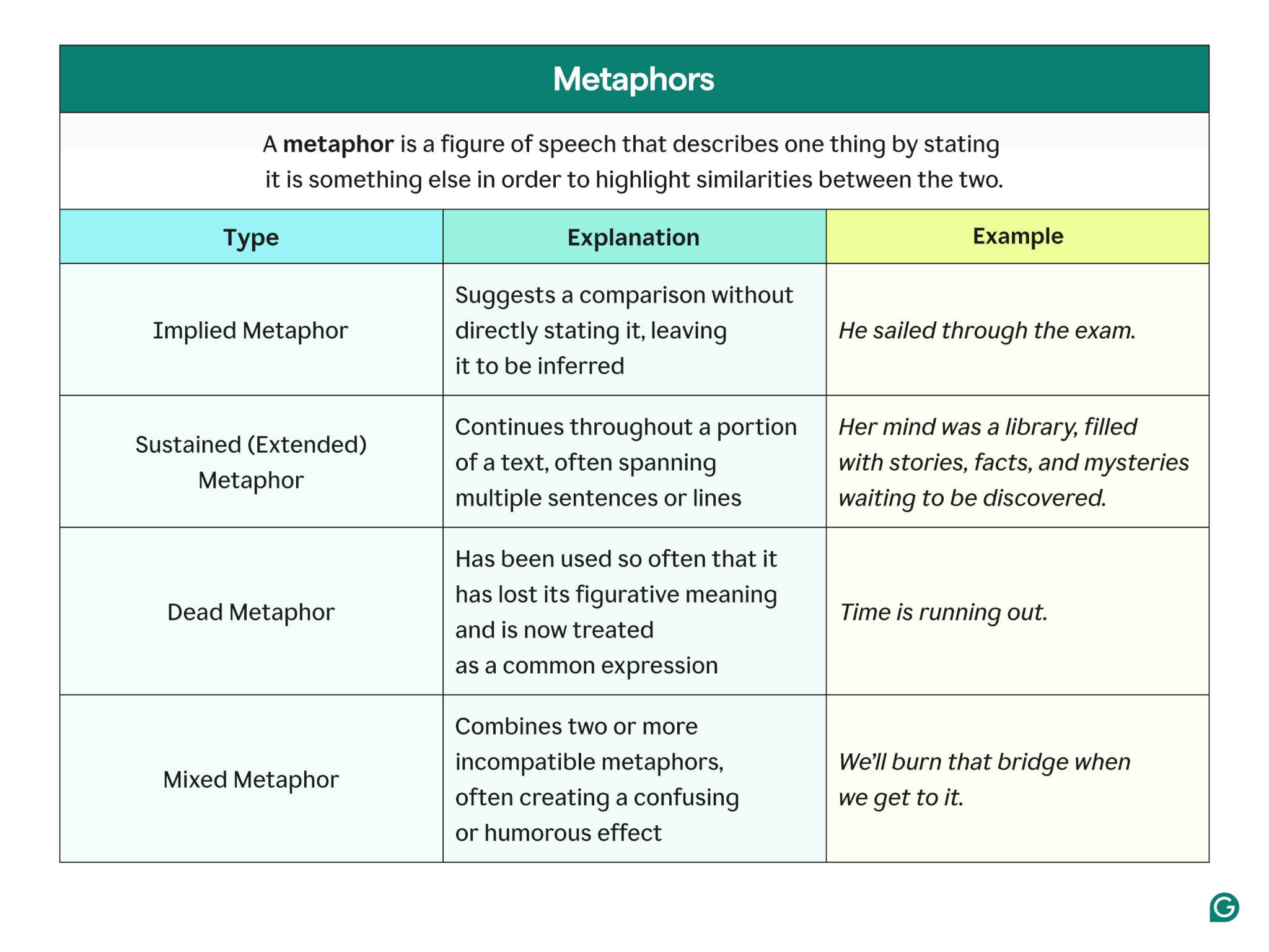
Implied metaphor
An implied metaphor departs from the “thing A is thing B” formula and allows you to make a more sophisticated and subtle type of comparison through implication.
Take these two examples:
Notice how, in the examples of implied metaphors above, the things being compared aren’t always mentioned—they’re implied. Mr. Alvarez is compared to a dog, but the word dog isn’t there. A movie scene is compared to a knife, but the word knife isn’t mentioned.
Implied metaphors are great for being poetic and creative, but make sure you’re not being too vague. People may misinterpret an implied metaphor if they can’t understand what you’re implying.
Sustained metaphor (extended metaphor)
A sustained or extended metaphor is carried through multiple sentences or even paragraphs. Because it is used and developed over a longer section of text, a sustained metaphor can be a powerful literary device that provides strong, vivid imagery in the reader’s mind.
This kind of metaphor is often found in songs and poetry. In a famous example from Shakespeare, Romeo compares Juliet to the sun over several lines.
But soft! What light through yonder window breaks? It is the East, and Juliet is the sun! Arise, fair sun, and kill the envious moon, Who is already sick and pale with grief.
Romeo is comparing Juliet to the sun, and if his speech ended after the second line, it would just be a regular metaphor. But over the following lines, Romeo keeps going, adding more references and comparisons that all revolve around Juliet being the sun, such as the moon being envious.
Dead metaphor
A dead metaphor is a cliché that has become so commonplace that the imagery has lost its power. When these metaphors were first used, they were clever and original. But with time (sometimes over centuries), they lost their freshness and impact.
Here are some examples of dead metaphors:
- raining cats and dogs
- spill the beans
- dead end
- hold your horses
Not all metaphors are good, and some can actually harm your writing. Like all clichés, dead metaphors come across as boring and banal to your audience.
Instead of repeating an old metaphor, reach a little further for an original image or think about ways to use a familiar metaphor in an unconventional way.
Mixed metaphor
A mixed metaphor uses two (or more) metaphors at the same time. While the meanings of the metaphors may or may not stay intact, using multiple metaphors at once can strain and confuse your audience.
The example above combines “get our ducks in a row” and “get on the same page.” Mixed metaphors are often mistakes made by people who have misheard or forgotten common metaphors.
Mixed metaphors can be pretty funny, however; the great Yogi Berra was famous for his “Yogi-isms,” which often contained bewilderingly mixed metaphors that still managed to get his point across:
But if you’re not trying to be funny, mixed metaphors can come off as awkward or even undermine the point you’re trying to make.
How to use metaphors
You don’t need anything except your imagination to come up with a good metaphor, but some added flair can go a long way. Remember, metaphors often represent something that is hard to take literally.
Consider the metaphor “rule with an iron fist” as an example. It would be a bit difficult to find a person with an actual hand made of iron. However, we are still able to interpret that metaphor as meaning someone who is hard and heavy-handed in governance.
When creating metaphors, stick to concepts that people are familiar with but may not necessarily associate with each other.
Here is a simple example:
You wouldn’t typically refer to your house as a circus, but this sentence implies that things are wild, full of excitement, and maybe a bit chaotic with Mom out of the house.
Here are some other tips for using metaphors.
Use metaphors sparingly
Metaphors can be powerful tools in writing, but some writers tend to overuse them. Using too many metaphors dilutes or weakens each one, taking away some of their impact and forcing your audience to figure out the meanings of one metaphor after another.
Instead, use metaphors sparingly so that each one achieves the maximum effect. Try to save metaphors for situations that are harder to explain, such as abstract concepts or emotions that are difficult to pinpoint.
Draw comparisons that aren’t obvious
Part of the appeal of metaphors is that they encourage the audience to think and engage their imagination. However, if a metaphor is too obvious, readers may overlook it without deeper consideration. To truly captivate your audience, aim for thought-provoking and original metaphors that inspire reflection and evoke strong imagery.
Anyone can compare life to a journey, but try to delve deeper to add more meaning to your metaphors. For example, you could use words like “sailing in turbulent waters” or “crossing a barren desert” when comparing life to a journey.
Avoid mixed metaphors
As mentioned above, it’s best to avoid using mixed metaphors in your writing. Mixing metaphors can add unnecessary confusion that detracts from a metaphor’s meaning. Use one metaphor at a time and space them out.
Metaphors in different types of writing
Metaphors are useful in both formal and informal writing, though their application varies depending on the context and purpose.
In creative writing, metaphors tend to be more artistic, drawing on emotions and feelings to form connections that aren’t obvious. Likewise, in marketing and advertising, metaphors can influence customers by making them feel a certain way, especially in slogans.
For example, the slogan of Disney’s theme parks, “Experience the magic,” is a metaphor. There’s no actual magic involved, but the metaphoric slogan suggests that people who come to the parks will feel something magical, encouraging them to visit.
Even in science or other nonfiction, metaphors can help explain concepts that are otherwise difficult to grasp.
For example, Stephen Hawking once said, “Not only does God play dice, but […] he sometimes throws them where they cannot be seen.” Although Hawking was an atheist, he used this religious metaphor to explain the randomness and mystery of the natural principles of science—something even the most intelligent people have trouble understanding.
Metaphor FAQs
What are metaphors?
Metaphors are figures of speech that compare two different things to help explain them better. The things aren’t literally the same, but they have some parts in common.
What is an example of a metaphor?
“All religions, arts, and sciences are branches of the same tree.” —Albert Einstein
How do you write a metaphor?
Metaphors work best when they connect abstract concepts to something familiar that readers already understand well. When coming up with your own metaphors, stick to ideas that people are familiar with but wouldn’t necessarily associate together.
What is the difference between a metaphor and a simile?
Metaphors and similes compare two different things, but similes use the words like or as, while metaphors do not. For example, “Marco is a busy bee” is a metaphor, but “Marco is as busy as a bee” is a simile.
Can metaphors be used in everyday language?
Yes, metaphors are commonly used in everyday language to convey complex ideas in a relatable way. For example, saying “time is a thief” implies that time steals moments from our lives, helping to express an abstract idea in a vivid and memorable way.






